Image-based Visual Servo Control for Aerial Manipulation Using a Fully-Actuated UAV
Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to perform high-altitude manipulation tasks beyond just passive visual application can reduce human workers’ time, cost, and risk. Prior research on aerial manipulation has relied on either ground truth state estimate or GPS/total station with some Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms, which may not be practical for many applications close to infrastructure with degraded GPS signal or featureless environments. Visual servo can eliminate the need to estimate robot pose. Existing works on visual servo for aerial manipulation either address solely end-effector position control or rely on precise velocity measurement and pre-defined visual guidance Furthermore, most of previous work used under-actuated UAVs, resulting in complicated mechanical and hence control designs for the end-effector. This paper develops an image-based visual servo control strategy for bridge maintenance applications using a fully-actuated UAV.
The main components are (1) a visual line detection and tracking system, (2) a hybrid force and motion controller based on an impedance force control system with estimated velocity using visual features. Our approach does not rely on either robot pose/velocity estimation from an external localization system or pre-defined visual guidance. The complexity of the mechanical system and controller architecture is also minimized due to the fully-actuated nature of the vehicle. To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first studies on aerial manipulation using visual servo that is capable of achieving both motion and force control without the need of external pose/velocity information or pre-defined visual guidance.

Main contributions of this work are:
-
We develop an image-based visual servo control strategy for bridge maintenance application using a fully-actuated UAV. Our approach does not rely on either robot pose/velocity estimation from an external localization system, such as GPS/motion capture system, or the pre-defined visual markers.
-
We develop a hybrid motion and impedance force controller so that the aerial manipulator can maintain constant force while tracking the lateral motion. Benefiting from the fully-actuated UAV platform, the complexity of the controller design gets reduced significantly.
-
We design an efficient line detection and tracking algorithm, which leverages the surface normal to provide the filtered surface. Our method can be run at a high computation rate, which is critical for real-time usage.
-
We present experiments to evaluate the whole motion tracking and force holding performance under visual guidance.
Painting Strategy
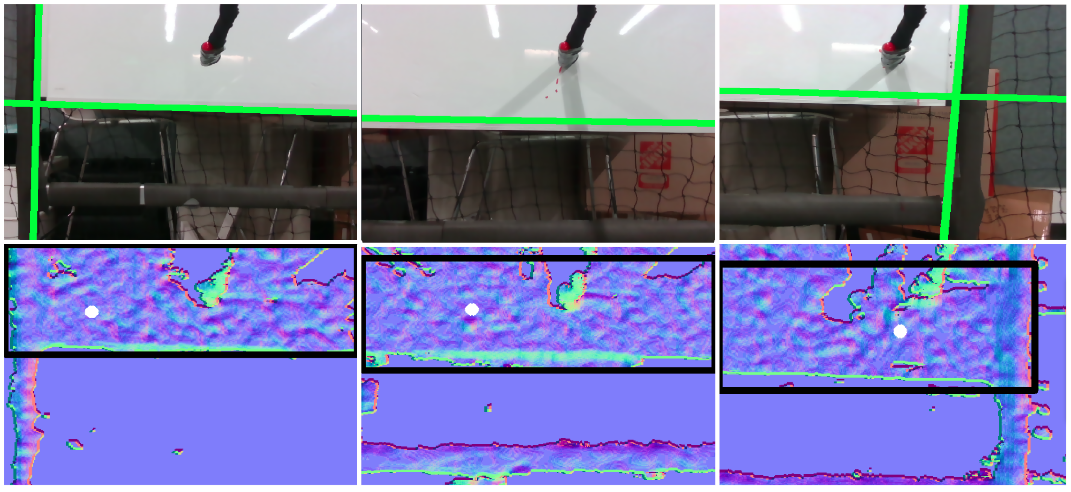
The vehicle first flies close to the bridge to a pre-selected starting point, such as the bottom right corner, under other guidance methods. Then, we switch to visual servo control by detecting and tracking the bottom edge (green line) and perform the painting from right to left. As the robot reaches the other side of the bridge, it starts tracking the vertical edge to move up and then switches to the lateral direction to paint back. During the painting process, the newly painted line generates new edges (horizontal red line), which serve as visual guidance for future painting.

We only leverage the visual line feature during the painting process without relying on external guidance to estimate vehicle pose or velocity. This indicates that the system needs a reliable line detection and tracking module to provide real-time visual feature. In addition, to satisfy the mission requirement – good painting quality in this scenario, the aerial manipulator needs to hold a constant force in the orthogonal direction of the bridge surface while maintaining an effective lateral motion.
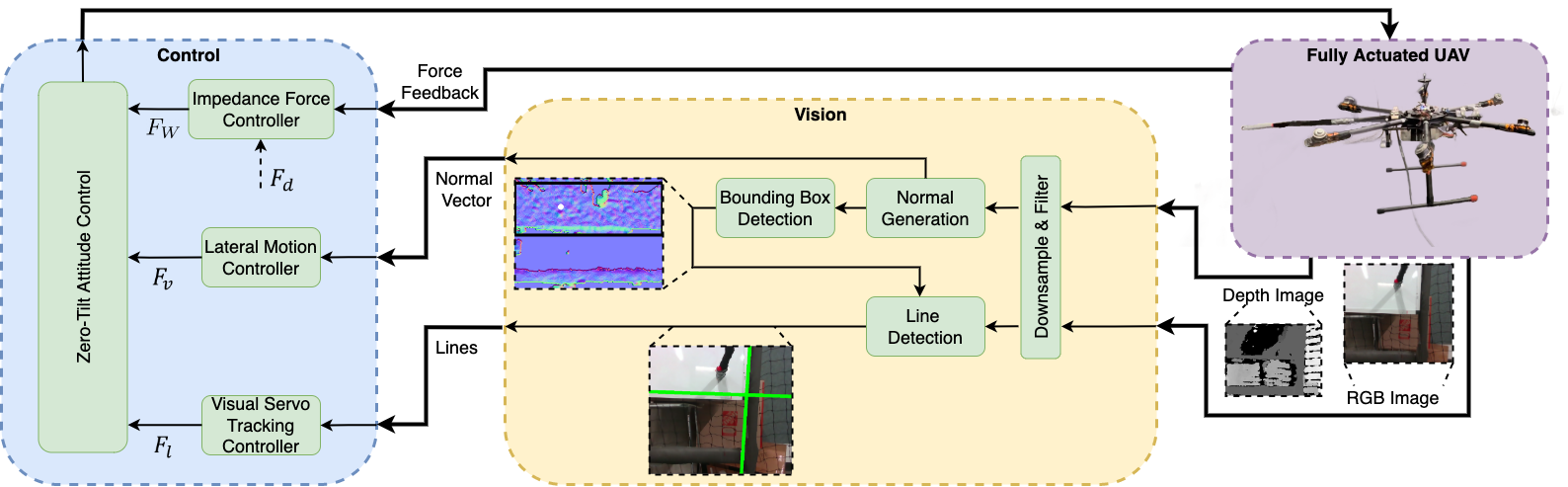
Hybrid Motion and Impedance Control System Based on Visual Line Guidance
we leverage the advantages of the fully-actuated UAV to design the control system. Based on our previous work, we select the zero-tilt attitude strategy to keep the vehicle’s tilt (roll and pitch) at zero at all times and stay completely horizontal during the flight. Thanks to the fully-actuated nature of our aerial manipulator. The control system is designed in a decoupled way, which consists of three major components: (1) an impedance force controller maintains a constant pushing force while the vehicle is moving; (2) an image-based visual-servo tracking controller ensures the motion of the end-effector is aligned with the detected visual line; (3) a lateral motion controller leverages the estimated velocity from the IMU information.
Line Detection and Tracking
We leverage the fact that the vehicle is always operating on the same surface and perform the filtering based on the surface normal. Our algorithm can be run at a high computation rate, which is critical for real-time usage. The overall algorithm consists of three main components: (1) Normal Image generation; (2) Bounding Box estimation; (3) Segmentation and Line detection.
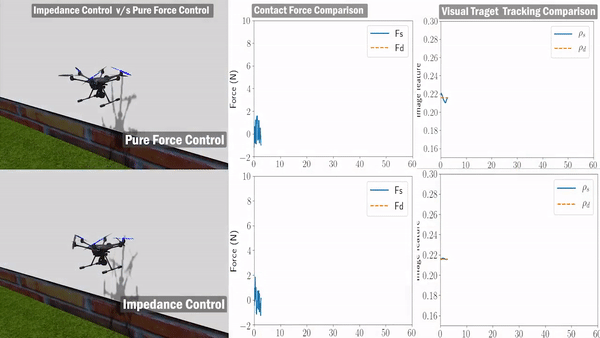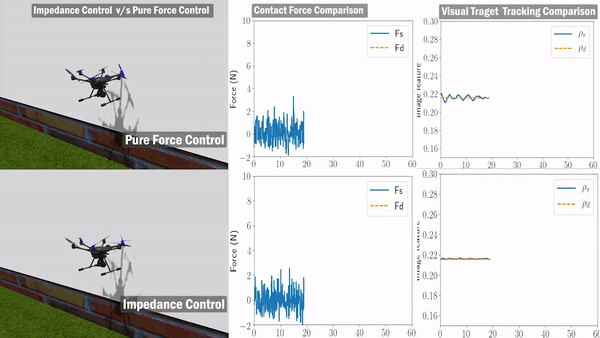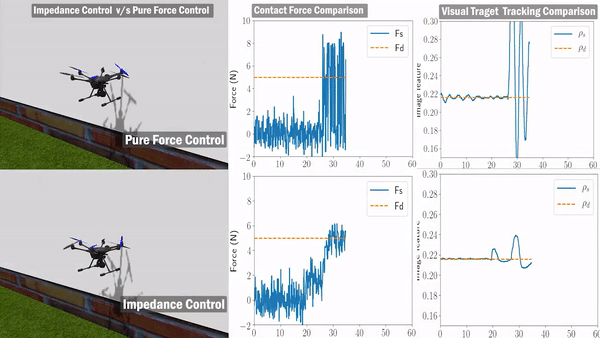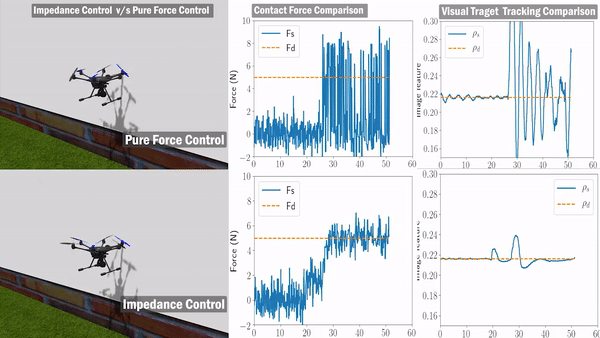
Validation
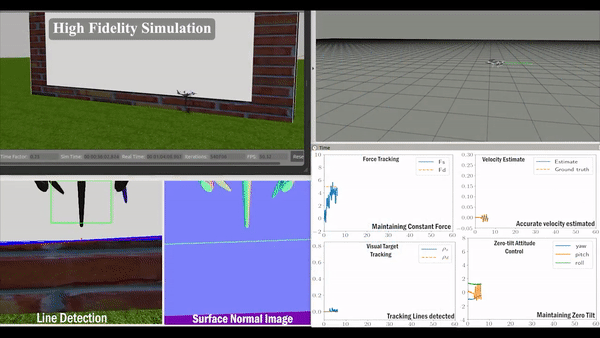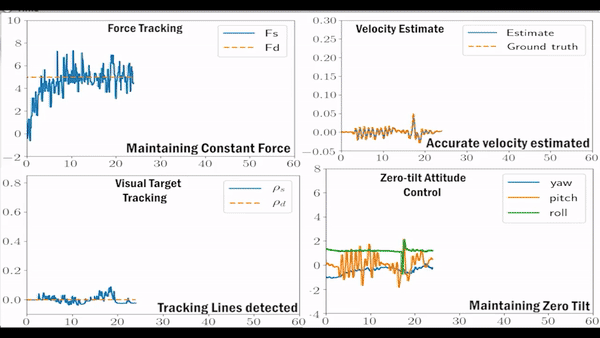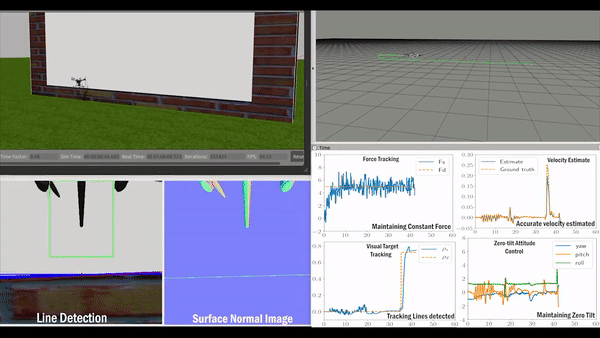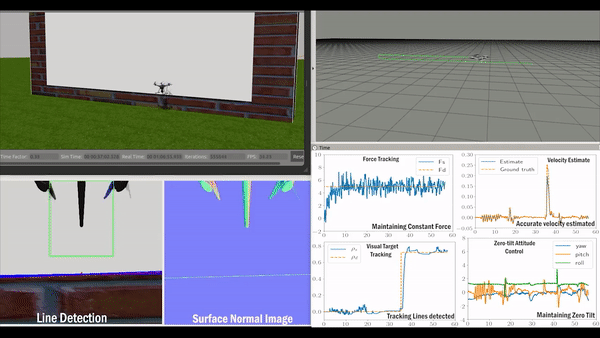
Related Paper
BibTeX:
@inproceedings{he2023image,
title={Image-based Visual Servo Control for Aerial Manipulation Using a Fully-Actuated UAV},
author={He, Guanqi and Janjir, Yash and Geng, Junyi and Mousaei, Mohammadreza and Bai, Dongwei and Scherer, Sebastian},
booktitle={2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
url={https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.16530.pdf},
year={2023},
organization={IEEE}
}

